- #1
Jurgen M
Model ground effect-vehicle shape like on picture fly above flat surface like floor sports hall or ice, wing end plates and trailing edge is so close to the ground(1mm) we can assume airlfow under the wing is zero and has stagnation pressure("100% ground effect").
How to calculate induced drag?
(Dont debate about stability,tail/rudder will fix this.I want analyze induced drag only for wing)
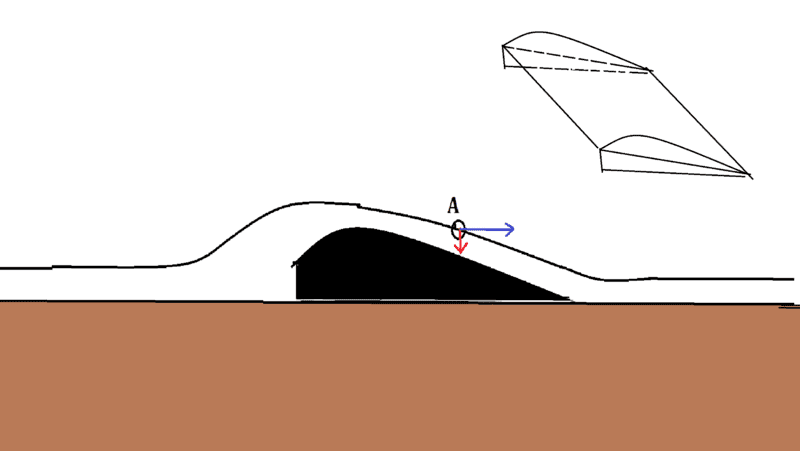
Here is some models
How to calculate induced drag?
(Dont debate about stability,tail/rudder will fix this.I want analyze induced drag only for wing)
Here is some models
Last edited by a moderator: