How to Solve a Multi-Atwood Machine Assembly
/
0 Comments
IntroductionThe figure on the right shows a "double-double" Atwood machine with three ideal pulleys and four masses. All pulleys are released from…

How to Apply Newton’s Second Law to Variable Mass Systems
Introduction
The applicability of Newton's second law in the oft-quoted "general form" $$\begin{align}\frac{d\mathbf{P}}{dt}=\mathbf{F}_{\text{ext}}\end{align}$$…
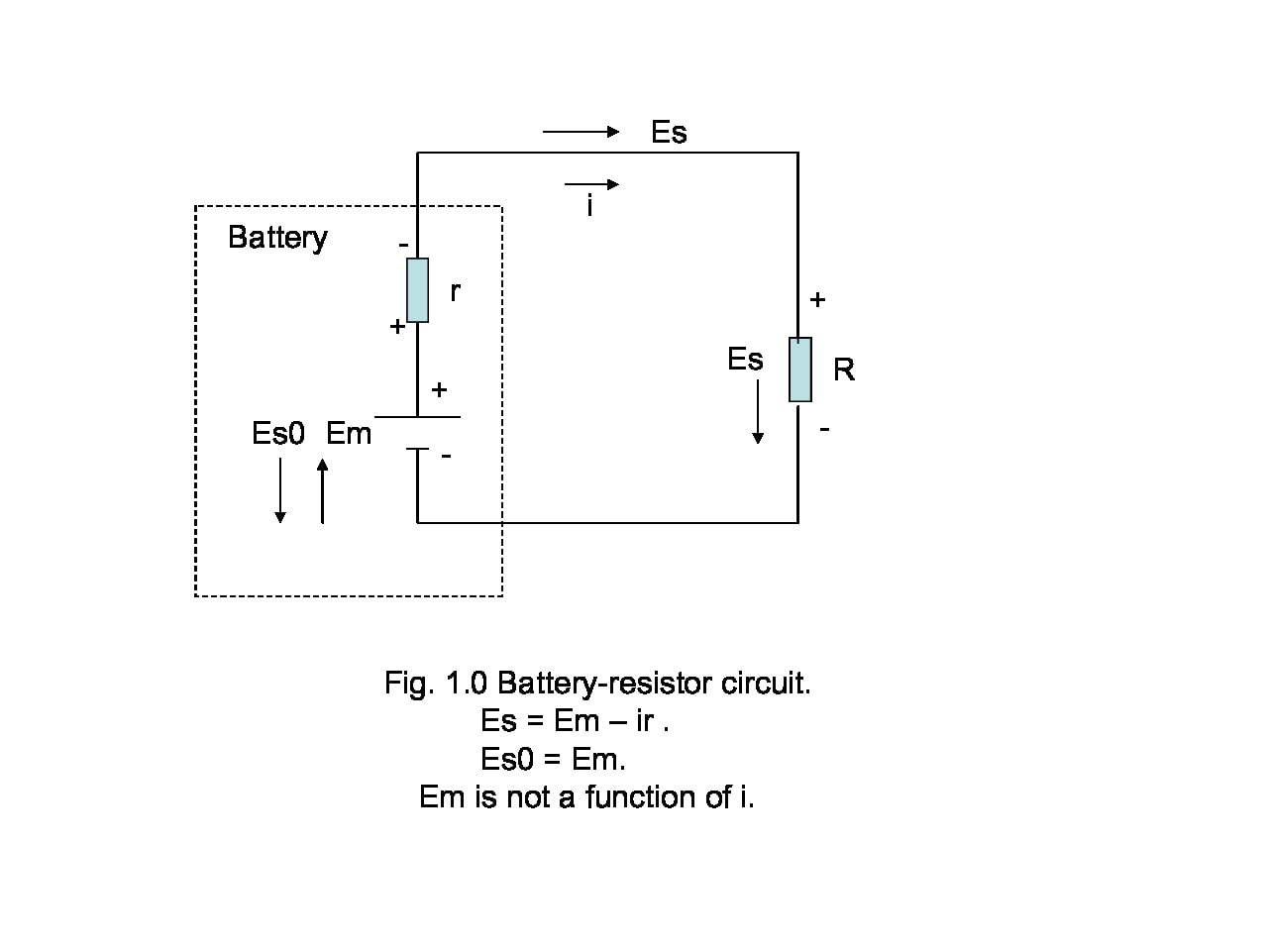
How to Measure Internal Resistance of a Battery
Introduction
A commonly encountered school-level Physics practical is the determination of the internal resistance of a battery - typically an AA or D…

Subtleties Overlooked in Friction Questions: Object Slides Down Ramp
Problem statement (simplified)
An object slides down a ramp at angle θ to encounter level ground. Both surfaces have kinetic friction: μ' on the ramp,…
How to Model a Magnet Falling Through a Conducting Pipe
Introduction
In an earlier article, we examined a magnet falling through a solenoid. We argued that the point dipole model can account for the basic features…
How to Model a Magnet Falling Through a Solenoid
Introduction
Modeling a magnet realistically is a task best done numerically. Even the simplified model of two separated disks with uniform surface…
Geodesic Congruences in FRW, Schwarzschild and Kerr Spacetimes
Introduction
The theory of geodesic congruences is extensively covered in many textbooks (see References); what follows in the introduction is a brief…

Corrections to MIT Open Courseware: Systems of Varying Mass
Corrections to
MIT Open Courseware 8-01sc classical mechanics,
fall 2016
Applying Newton's Laws to systems of Varying Mass
PDF Course Link
My concerns…
Quaternions in Projectile Motion
Introduction
In a previous Physics Forums article entitled “How to Master Projectile Motion Without Quadratics”, PF user @kuruman brought to our…
How to Solve Projectile Motion Problems in One or Two Lines
Introduction
We show how one can solve most, if not all, introductory-level projectile motion problems in one or maybe two lines. To this end, we forgo…

Maximizing Horizontal Range of a Projectile
Introduction
A recent homework problem that appeared in the forums was concerned with maximizing the horizontal range of a projectile subject to the launch…

A Numerical Electromagnetic Solver Using Duality
In the previous insights article (How to Use Duality in Computational Electromagnetic Problems), I covered some uniqueness theorems for the Riemann-Silberstein…
The Electric Field Seen by an Observer: A Relativistic Calculation with Tensors
This Insight was inspired by the discussion in "electric field seen by an observer in motion", which tries to understand the relation between two expressions:…
Valentine’s Reflections: Mathematical Matters of the Heart
Introduction
Being a somewhat geeky Maths 'nerd', I spent days leading up to Valentine's day trying to find a Maths function appropriate to the day. In…

How to Use Duality in Computational Electromagnetic Problems
Some weeks ago I happened across a post that caught my eye. Dale asked a question about the number of photons in an electromagnetic field. His question…

Equations of Motion Revisited
Introduction
In any school Physics course, the Newtonian equations of motion are very much a 'stock' item. Students learn the equations and are given…
How to Master Projectile Motion Without Quadratics
Introduction
In a homework thread a while back a PF member expressed dismay along the lines of "oh no, not another boring projectile motion problem."…

Intro to Physically Reasonable Waves on a String
Introduction
Physics teachers who are either writing physics questions that deal with waves on a string or setting up equipment for a class lab or demo…

An Alternate Approach to Solving 2-Dimensional Elastic Collisions
Introduction
This article follows on from the previous on an alternate approach to solving collision problems. In that article, we determined the equal…
How to Recognize Split Electric Fields
Introduction
In a previous Insight, A New Interpretation of Dr. Walter Lewin’s Paradox, I introduced the fact that there are two kinds of E fields. …
An Introduction to the Generation of Mass from Energy
Introduction
This article is essentially an addition to the previous one on (mainly) inelastic collisions to include the particular case of inelastic…
An Alternative Approach to Solving Collision Problems
Introduction
Collisions are very much a stock item in any school physics curriculum and students are generally taught about the use of the principles…
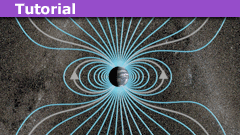
Maxwell’s Equations in Magnetostatics and Solving with the Curl Operator
Introduction:
Maxwell's equation in differential form ## \nabla \times \vec{B}=\mu_o \vec{J}_{total}+\mu_o \epsilon_o \dot{\vec{E}} ## with ## \dot{\vec{E}}=0…
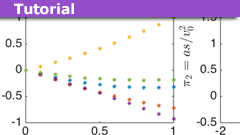
Learn the Basics of Dimensional Analysis
As a university teacher and as a PF member, I have often noted that students are largely unaware of or not using dimensional analysis to help them in their…

The Classical Limit of Quantum Mechanical Commutator
The Classical Limit of Commutator (without fancy mathematics)
Quantum mechanics occupies a very unusual place among physical theories: It contains classical…
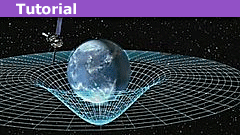
Understanding Precession in Special and General Relativity
The Absolute Derivative
In relativity we typically deal with two types of quantities: fields, which are defined everywhere, and particle properties, which…

A Formal Definition of Large-Scale Isotropy
This Insight is part of my attempt to develop a formal definition of 'large-scale isotropy', a concept that is fundamental to most cosmology, but that…
Exploring Fermi-Walker Transport in Kerr Spacetime
In the last two posts in this series, we developed some tools for looking at Fermi-Walker transport in Minkowski spacetime and then applied them in Schwarzschild…
Learning Fermi-Walker Transport in Schwarzschild Spacetime
In the first post in this series, we introduced the concepts of frame field, Fermi-Walker transport, and the "Fermi derivative" of a frame field, and developed…

Fermi-Walker Transport in Minkowski Spacetime
This is the first of several posts that will develop some mathematical machinery for studying Fermi-Walker transport. In this first post, we focus on Minkowski…

An Example of Servo-Constraints in Mechanics
Servo-constraint was invented by Henri Beghin in his Ph.D. thesis in 1922. For details see the celebrated monograph in rational mechanics by Paul Appell.To…

Learn Orbital Mechanics in Unity Game Engine for Augmented Reality
In this Insight, I’ll go over implementing basic orbital mechanics simulations in the Unity game engine as well as an approach to scaling the simulation…

A New Interpretation of Dr. Walter Lewin’s Paradox
Much has lately been said regarding this paradox which first appeared in one of W. Lewin's MIT lecture series on ##{YouTube}^{(1)}##. This lecture was…

How to Calculate the Spin of Black Hole Sagittarius A*
This Insight takes a look at how it is possible to calculate the spin of Sagittarius A*, the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way using…

How to Solve Einstein’s Field Equations in Maxima
A few months ago, pervect pointed me to a post by Chris Hillman which is an introduction to the usage of Maxima for General Relativity. Maxima is a free…
Rindler Motion in Special Relativity: Rindler Coordinates
Our destination
In our last article, Hyperbolic Trajectories, we derived some facts about the trajectory of a rocket that is undergoing constant (proper)…
Rindler Motion in Special Relativity: Hyperbolic Trajectories
Introduction: Why Rindler Motion?
When students learn relativity, it's usually taught using inertial (constant velocity) motion. There are lots of reasons…

Learn Statistical Mechanics: Equilibrium Systems
This is the first of a multi-part series of articles intended to give a concise overview of statistical mechanics and some of its applications. These articles…

Learn an Integral Result from Parseval’s Theorem
Introduction:
In this Insight article, Parseval's theorem will be applied to a sinusoidal signal that lasts a finite period of time. It will be shown…
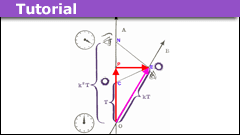
Learn Relativity Using the Bondi K-calculus
Although Special Relativity was formulated by Einstein (1905), and given a spacetime interpretation by Minkowski (1908) [which helped make special relativity…
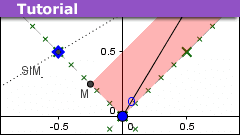
Relativity Variables: Velocity, Doppler-Bondi k, and Rapidity
Traditional presentations of special relativity place emphasis on "velocity", which of course has an important physical interpretation... carried over…
Frames of Reference: Linear Acceleration View
My previous Insight, Frames of Reference: A Skateboarder's View, explored mechanical energy conservation as seen from an inertial frame moving relative…

Fabry-Perot and Michelson Interferometry: A Fundamental Approach
Fabry-Perot Effect:
The Fabry-Perot effect is usually treated in most optics textbooks as the interference that results from multiple reflections of the…
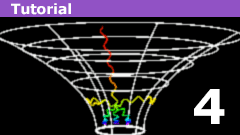
The Schwarzschild Geometry: Physically Reasonable?
In the last article, we looked at various counterintuitive features of the Schwarzschild spacetime geometry, as illustrated in the Kruskal-Szekeres…
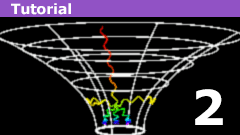
The Schwarzschild Geometry: Coordinates
At the end of part 1, we looked at the form the metric of the Schwarzschild geometry takes in Gullstrand-Painleve coordinates:$$
ds^2…
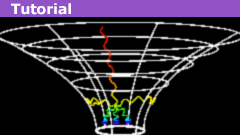
The Schwarzschild Geometry: Key Properties
Not long after Einstein published his Field Equation, the first exact solution was found by Karl Schwarzschild. This solution is one of the…

Learn The Basics of Rolling Motion
Although rolling wheels are everywhere, when most people are asked "what is the axis of rotation of a wheel that rolls without slipping?", they will answer…

How to Determine the Change in Entropy
How do you determine the change in entropy for a closed system that is subjected to an irreversible process?Here are some typical questions we get…
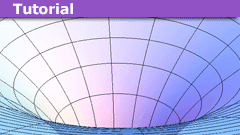
Learn Orbital Precession in the Schwarzschild and Kerr Metrics
The Schwarzschild Metric
A Lagrangian that can be used to describe geodesics is [itex]F = g_{\mu\nu}v^\mu v^\mu[/itex], where [itex]v^\mu = dx^\mu/ds[/itex]…

Learn About Tetrad Fields and Spacetime
A spacetime is often described in terms of a tetrad field, that is, by giving a set of basis vectors at each point. Let the vectors of the tetrad be denoted…
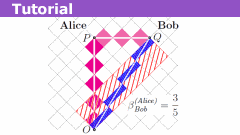
Learn About Relativity on Rotated Graph Paper
This Insight is a follow-up to my earlier tutorial Insight (Spacetime Diagrams of Light Clocks).
I gave it a different name because I am placing more…

Learn Basic Kinematics in Classical Mechanics
There is an interesting thing in teaching of Classical Mechanics. Several theorems which presented below form a core part of kinematics for all Russian…

Presenting a Rare Kinematic Formula
Here we present some useful kinematic fact which is uncommon for textbooks in mechanics.
Consider a convex rigid body (RB) rolling without slipping…
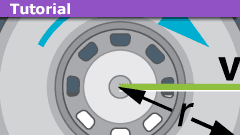
Elementary Construction of the Angular Velocity
Physics books seldom contain an accurate definitions of the angular velocity of a rigid body. I believe that the following construction is as simple as…

Frequently Made Errors in Vectors – Elementary Use
A vector has magnitude and direction. Pictorially, a vector can be imagined as a location in n-dimensional space relative to some fixed origin. …
LightCone 8 Tutorial Part III – How Things are Computed
In Part I and Part II of this mini-series, we have briefly discussed the basic user interface and the use of charts to depict the LCDM cosmological model.…

LightCone8 Tutorial Part II – Charts
Part I dealt with the basic user interface of LightCone8. This part of the tutorial is about potentially useful cosmological insights to be gained from…

LightCone8 Tutorial Part I
LightCone 8 is a versatile tabulating/charting cosmological calculator, useful for understanding the expansion history of the universe (and even some future…
An Equation for the Centrifugal Force Reversal Near A Black Hole
My goal in this article is to derive a simple equation for the proper acceleration of an observer traveling on a circular path around a Schwarzschild black…
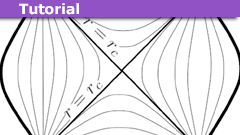
Learn A Short Proof of Birkhoff’s Theorem
Birkhoff's theorem is a very useful result in General Relativity, and pretty much any textbook has a proof of it. The one I first read was in Misner, Thorne,…
Frequently Made Errors in Heat: Elementary Level
1. Heat, Work, Internal Energy, and Kinetic Energy
"If heat is the motion of molecules, why isn't it Kinetic Energy?"In everyday use, we may think…
Frequently Made Errors: Pseudo and Resultant Forces
1. Real versus Fictitious
Pseudo, or "fictitious", forces can arise when a non-inertial frame of reference is used. Using a non-inertial frame…

Why Renormalisation in Quantum Theory Needs a Cutoff
Introduction
This is a follow on from my paper explaining renormalization. A question was raised - why exactly do we need a cut-off. There is a deep reason…

Frequently Made Errors in Mechanics: Springs
1. Springs in Series
"A spring of constant ##k_1## is connected in series with a spring of constant ##k_2##. What is the spring constant…

Frequently Made Errors in Mechanics: Momentum and Impacts
An impact is an impulse (change of momentum) that involves arbitrarily large forces acting very briefly. These result in near-instantaneous…

Frequently Made Errors in Mechanics: Hydrostatics
1. Archimedes' Principle
X "When a body is placed in a liquid, the weight of the body equals the weight of the liquid displaced"That will…
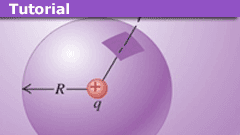
Learn a Partial “Derivation” of Gauss’s Law
Gauss's law was formulated by Carl Friedrich Gauss in 1835. It is one of the four Maxwell's equations that form the basis of classical electrodynamics.…

Frequently Made Errors in Equation Handling
1. Algebra versus Arithmetic
When numerical values are provided as inputs in a question, it is tempting to plug these into the equations…

Frequently Made Errors in Mechanics: Kinematics
Kinematics is the subset of dynamics that only concerns itself with time, displacement, velocity, and acceleration. A problem is…

Frequently Made Errors in Mechanics: Moments
The term "moment" is used in various ways in Physics and Mathematics:Given a force and a reference point, the force has a moment (or…

Quantum Renormalisation Made Easy
What Is The Issue With Renormalisation
If you have an interest in physics you have likely come across renormalisation before, although what it really…
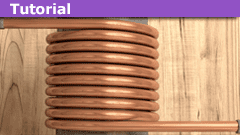
Misconceiving Mutual Inductance Coefficients
A commonly used formula for mutual inductance M between two nearby coils L1 and L2 is M = k√(L1*L2). This formula however assumes equal percentage…

Frequently Made Errors in Mechanics – Friction
1. Direction of the normal
Definition: The normal force that body A exerts on body B is that force of minimum magnitude which suffices to…

Frequently Made Errors in Mechanics: Forces
Notation: On this page, a circumflex signifies an average.
1. Forces as vectors
A force is a vector, i.e. has magnitude and direction.…
How to Visualize the 2-D Particle in a Box
Introduction
The particle in a box is a staple of entry-level Quantum Mechanics classes because it provides a meaningful contrast between classical and…

Understanding Entropy and the 2nd Law of Thermodynamics
Introduction
The second law of thermodynamics and the associated concept of entropy have been sources of confusion to thermodynamics students for centuries.…
